The space industry is undergoing a transformative era, with private companies like Rocket Lab (RKLB) leading the charge in making space more accessible. At the heart of this revolution is the Neutron rocket, a medium-lift launch vehicle set to debut in the second half of 2025. As the demand for satellite constellations and deep space missions grows, Neutron promises to deliver cost-effective and reliable launch services. For investors, the rocket’s success could significantly impact RKLB stock, while space enthusiasts are eager to see how it reshapes the industry. This article dives into the Neutron rocket’s specifications, development progress, strategic importance, and its potential influence on Rocket Lab’s financial future, offering a comprehensive guide to this groundbreaking project.
What is the Neutron Rocket?
The Neutron rocket is Rocket Lab’s next-generation, partially reusable, medium-lift launch vehicle, designed to meet the growing needs of the commercial and government space sectors. Unlike the company’s Electron rocket, which focuses on small satellite launches, Neutron targets larger payloads, making it suitable for mega constellation deployments, interplanetary missions, and potentially human spaceflight.
Specifications and Features
The Neutron rocket boasts impressive technical specifications, positioning it as a competitive player in the medium-lift market:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Height | 43 meters (141 feet) |
| Diameter | 7 meters |
| Fairing Diameter | 5 meters |
| Payload to LEO | 13,000 kg (28,700 lb) |
| Payload to Mars/Venus | 1,500 kg |
| Lift Off Mass | 480,000 kg |
| Propellant | Liquid Oxygen (LOX) / Methane |
| First Stage | 9 Archimedes Engines, Total Lift-off Thrust: 1,485,000 lbf |
| Second Stage | Single Vacuum Archimedes Engine, Vacuum Thrust: 890 kN (200,000 lbf) |
Key Features:
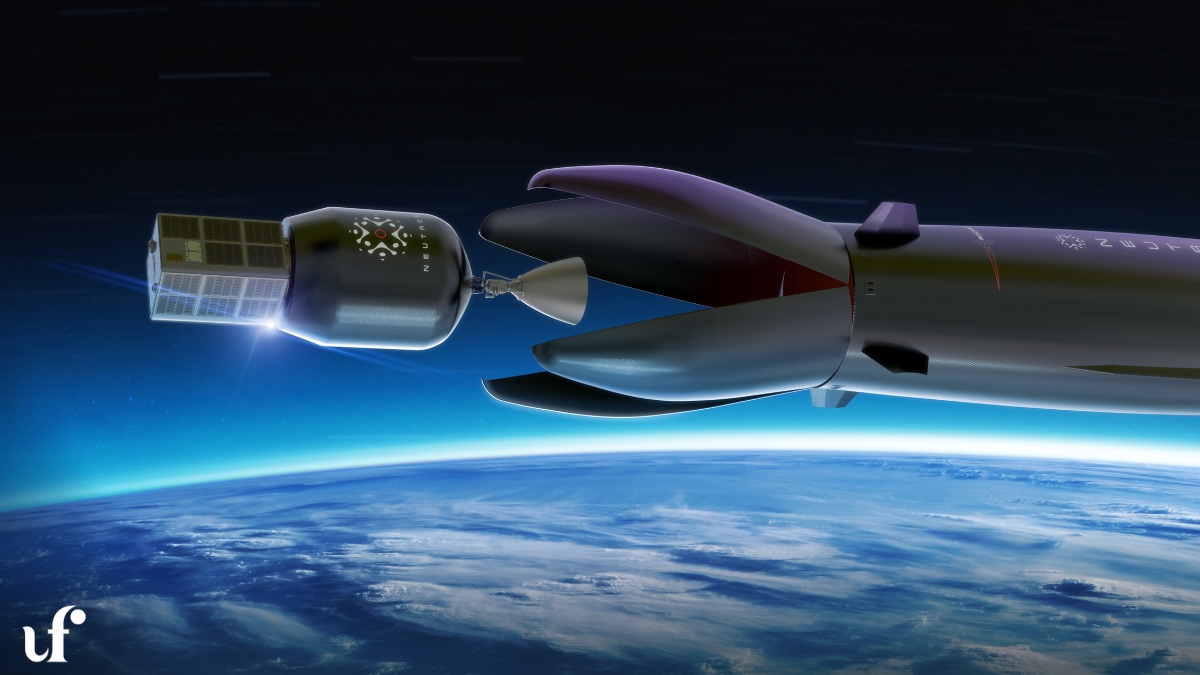
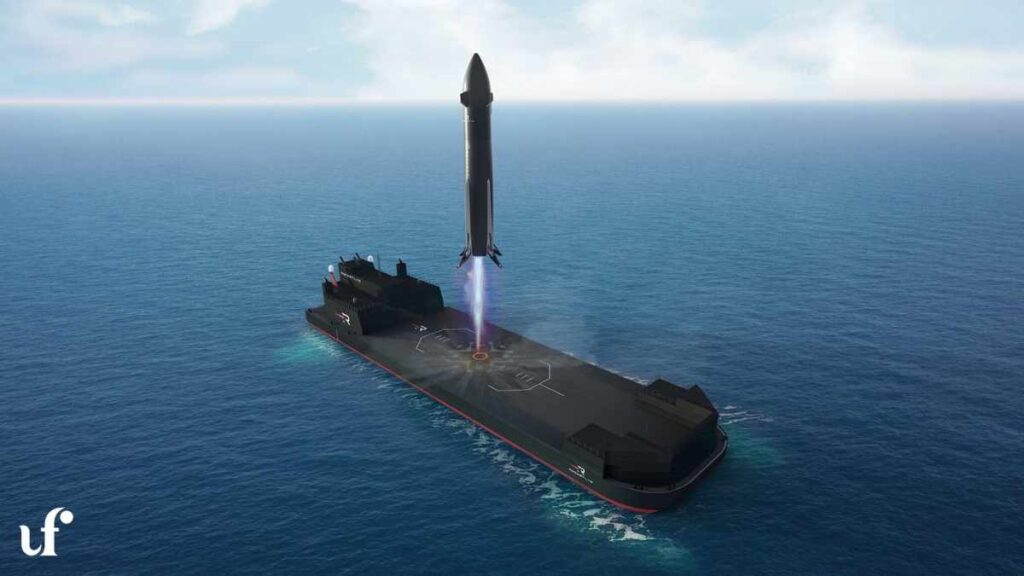
- Reusability: The first stage is designed to return to the launch site or land on a floating platform named “Return On Investment,” reducing launch costs.
- Captive Fairing Design: Unlike traditional rockets, Neutron’s fairing remains attached to the first stage, simplifying recovery and enhancing reusability.
- Carbon Composite Structure: Lightweight materials improve performance and efficiency.
- Archimedes Engines: Powered by LOX and methane, these engines are optimized for reliability and cost-effectiveness.
The rocket’s unique “hippo” mouth fairing, which deploys the upper stage by opening like a jaw, is a novel design that sets it apart from competitors. This innovation, combined with its reusable first stage, aims to make Neutron a cost-competitive option for a wide range of missions.
Comparison with SpaceX’s Falcon 9
The Neutron rocket is often compared to SpaceX’s Falcon 9, a well-established medium-lift rocket. Here’s how they stack up:
| Feature | Neutron (Rocket Lab) | Falcon 9 (SpaceX) |
|---|---|---|
| Payload to LEO | 13,000 kg | 22,800 kg |
| Reusability | First stage reusable, captive fairing | First stage reusable, detachable fairing |
| Height | 43 meters | 70 meters |
| Propellant | LOX / Methane | LOX / RP-1 (Kerosene) |
| Launch Cost (Estimated) | ~$50–55 million per launch | ~$60–90 million per launch |
While Falcon 9 has a higher payload capacity and a proven track record, Neutron’s smaller size and innovative design make it ideal for customers needing dedicated launches to specific orbits. Rocket Lab aims to offer more frequent and flexible launch options, potentially carving out a niche in the competitive market dominated by SpaceX.
Development Progress and Milestones
Rocket Lab has made significant strides in developing the Neutron rocket since its announcement on March 1, 2021. The company is on track for its first launch in the second half of 2025, with several key milestones achieved:
- 2023: Construction of the first full-scale carbon composite tank for the second stage began, alongside structural and cryogenic testing. The first Archimedes engine was completed, marking a critical step in propulsion development.
- 2024: Successful hot fire tests of the Archimedes engine at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, reaching 102% power. The second stage completed qualification testing, including 1.3 million pounds of tensile force and cryogenic conditions. The first stage’s outer shell and reusable fairings were also qualified.
- 2025: Regulatory approval was granted for launches from Launch Complex 3 at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport in Wallops Island, Virginia. Rocket Lab selected Bollinger Shipyards to modify a 400-ft-long landing platform, “Return On Investment,” for first-stage recovery, with delivery expected in early 2026.
Recent updates, including posts on X from July 2025, confirm that Rocket Lab is moving “full steam ahead” to bring Launch Complex 3 online for the Neutron launch. The company has also secured contracts, such as a multi-launch agreement with a commercial satellite operator and a U.S. Air Force contract for a point-to-point cargo test flight in 2026, demonstrating confidence in Neutron’s capabilities.
Read More: – Bitcoin Price Hike: What’s Driving the Surge in 2025?
Rocket Lab’s Strategy and Market Position
Founded in 2006 by Peter Beck, Rocket Lab has established itself as a leader in the small satellite launch market with its Electron rocket, which has completed numerous successful missions since its debut in 2017. The company’s mission is to “remove barriers to commercial space,” and Neutron is a critical part of this vision.
From Electron to Neutron
The Electron rocket, designed for small payloads up to 300 kg, has made Rocket Lab a go-to provider for CubeSat and small satellite launches. With over 50 launches by mid-2025, Electron is the second most frequently flown U.S. orbital rocket. However, the growing demand for larger payloads, particularly for mega constellations, prompted Rocket Lab to develop Neutron.
Neutron expands Rocket Lab’s capabilities, allowing it to compete with larger players like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and United Launch Alliance. By offering a medium-lift rocket with reusable components, Rocket Lab aims to capture a significant share of the $5.6 billion National Security Space Launch (NSSL) program and commercial markets.
Strategic Acquisitions and Expansion
Rocket Lab has bolstered its capabilities through strategic acquisitions, including:
- Advanced Solutions, Inc. (2021): Enhanced spacecraft flight software.
- Planetary Systems Corporation (2021): Added satellite separation systems.
- SolAero (2022): Strengthened space solar power products.
- Geost (2025): Expanded into payload development, positioning Rocket Lab as a vertically integrated space solutions provider.
These acquisitions, combined with investments in U.S.-based manufacturing facilities, such as the Space Structures Complex in Maryland, underscore Rocket Lab’s commitment to scaling its operations.

Impact on RKLB Stock
The development of the Neutron rocket is a pivotal factor for RKLB stock, as it positions Rocket Lab to tap into new revenue streams and compete in high-value markets. In Q2 2025, RKLB stock surged 164% from $14.71 to $38.88, driven by:
- Strong Q1 2025 revenue of $122.6 million, up 32% year-over-year.
- A backlog exceeding $1.07 billion, reflecting customer confidence.
- Major defense contracts, including selection for the NSSL Phase 3 Lane 1 program.
- The acquisition of Geost, enhancing Rocket Lab’s end-to-end offerings.
Analysts are optimistic about Rocket Lab’s future, with a consensus “Buy” rating and a 12-month price target of $29.33 as of July 2025, though some project targets as high as $54.50 by 2026. The company’s $428 million cash runway supports ongoing R&D, particularly for Neutron, despite short-term EBITDA losses.
However, investors should consider risks:
- Development Delays: Some analysts, like Bleecker Street Research, have questioned the feasibility of the 2025 launch timeline, suggesting potential delays to 2026 or later.
- Competition: SpaceX’s dominance and other competitors like Antares and Soyuz pose challenges.
- Market Volatility: The space sector is inherently volatile, impacting stock performance.
Despite these risks, Rocket Lab’s operational momentum and strategic positioning make RKLB stock an attractive long-term investment for those bullish on the space economy.
Also Read: – USPS Stamp Price Hike 2025: New Rates & What It Means
What’s New in 2025
The year 2025 has been a landmark for Rocket Lab and the space industry:
- Neutron Progress: Regulatory approval for Launch Complex 3 and ongoing modifications to the “Return On Investment” landing platform signal readiness for the 2025 launch.
- Defense Contracts: Selection for the U.S. Air Force’s point-to-point cargo test flight in 2026 highlights Neutron’s versatility.
- Industry Trends: The space economy is projected to grow significantly, driven by satellite constellations and deep space exploration, positioning Rocket Lab favorably.
Rocket Lab’s inclusion in the Russell 1000 and a NASA streaming partnership further enhance its visibility and credibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the payload capacity of the Neutron rocket?
2. When is the first launch of the Neutron rocket scheduled?
3. How does the Neutron rocket compare to SpaceX’s Falcon 9?
4. What are the key features that make the Neutron rocket unique?
• Reusability: The first stage returns to the launch site or lands on a floating platform, reducing costs.
• Captive Fairing: The “hippo” mouth fairing stays attached to the first stage, simplifying recovery.
• Carbon Composite Structure: Lightweight materials enhance efficiency and performance.
• Archimedes Engines: Powered by LOX and methane, these engines are designed for reliability and cost-effectiveness.
These features make Neutron a forward-thinking solution for the modern space industry, addressing the need for affordable and frequent launches. The rocket’s design reflects Rocket Lab’s experience with the Electron, scaling up innovation for larger missions.
5. How will the Neutron rocket impact Rocket Lab’s business and stock?
6. What are the risks associated with investing in RKLB stock?
• Development Risks: Delays in Neutron’s 2025 launch could impact financial projections and investor confidence.
• Competition: SpaceX’s dominance and other competitors like Antares and Soyuz challenge Rocket Lab’s market share.
• Financial Losses: Current EBITDA losses due to R&D spending may persist until Neutron generates revenue.
• Market Volatility: The space sector’s high-risk nature can lead to stock price fluctuations.
Despite these risks, Rocket Lab’s strong backlog, cash reserves, and strategic positioning suggest significant growth potential for investors willing to navigate the uncertainties.
Conclusion
The Neutron rocket is a cornerstone of Rocket Lab’s vision to democratize space access. With its innovative design, reusability, and competitive pricing, Neutron is poised to challenge industry leaders and meet the growing demand for satellite launches and deep space missions. As Rocket Lab prepares for the 2025 debut, the rocket’s success could propel RKLB stock to new heights, offering investors a chance to capitalize on the expanding space economy. For space enthusiasts and investors alike, staying informed about Rocket Lab’s progress is crucial. Share your thoughts in the comments, subscribe to our newsletter for updates, or follow Rocket Lab on social media to stay in the loop.